Life Insurance Basics_ A Beginner's Guide
Understanding Life Insurance The Foundation of Financial Security
Life insurance. The very words can conjure up images of complicated paperwork, solemn conversations, and a general feeling of unease. But let’s break that down. Life insurance, at its core, is a contract. You, the policyholder, pay premiums to an insurance company. In exchange, the company promises to pay a lump sum of money, known as a death benefit, to your designated beneficiaries upon your death. Think of it as a safety net, a financial cushion designed to protect your loved ones when you're no longer around to provide for them.
Why is it so important? Well, consider the potential financial burdens your family might face without your income. Mortgage payments, childcare costs, education expenses, everyday living expenses – these can quickly become overwhelming. Life insurance helps alleviate that burden, providing a financial lifeline during a difficult time. It's not about you; it's about ensuring the well-being of those you care about most.
Different Types of Life Insurance Policies Exploring Your Options
The world of life insurance can seem like a maze of acronyms and jargon. Term life, whole life, universal life, variable life – it's enough to make your head spin! Let's simplify things by focusing on the two main categories: term life insurance and permanent life insurance.
Term Life Insurance Affordable Protection for a Specific Period
Term life insurance is like renting an apartment. You pay premiums for a specific period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. If you die within that term, your beneficiaries receive the death benefit. If you outlive the term, the coverage expires. Term life is generally more affordable than permanent life insurance, making it a popular choice for young families or individuals on a budget. It's a great option for covering specific financial obligations, such as a mortgage or college tuition.
Think of it this way: you're buying protection for a defined period when your financial responsibilities are at their peak. Once the kids are grown, the mortgage is paid off, and you've accumulated significant savings, the need for term life insurance may diminish.
Permanent Life Insurance Lifelong Coverage with a Cash Value Component
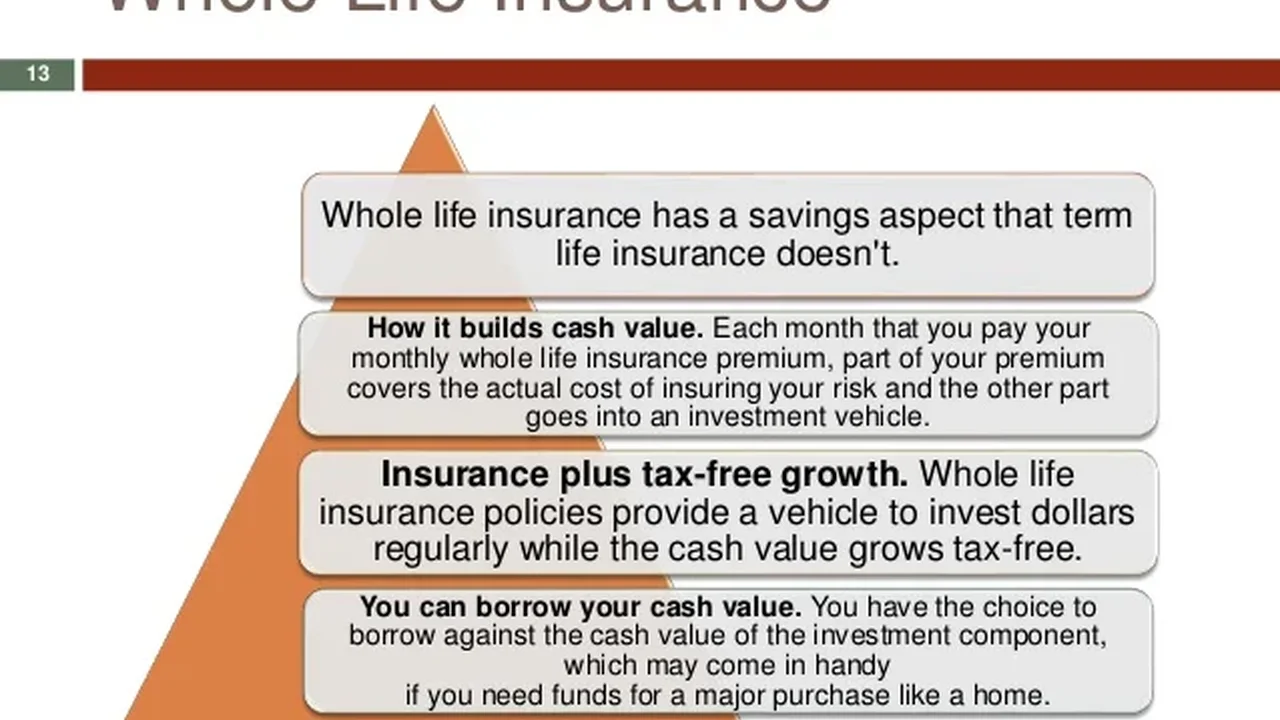
Permanent life insurance, on the other hand, is like buying a house. It provides lifelong coverage and includes a cash value component that grows over time. This cash value can be borrowed against or withdrawn, providing a potential source of funds for future needs. There are several types of permanent life insurance, including whole life, universal life, and variable life.
Whole Life Insurance: This type offers a guaranteed death benefit and a guaranteed rate of return on the cash value. Premiums are typically level, meaning they remain the same throughout the life of the policy. Whole life is a conservative option, offering stability and predictability.
Universal Life Insurance: This type offers more flexibility than whole life. Premiums can be adjusted within certain limits, and the cash value grows based on current interest rates. Universal life can be a good option for those who want more control over their policy.
Variable Life Insurance: This type allows you to invest the cash value in a variety of investment options, such as stocks and bonds. The death benefit and cash value can fluctuate based on the performance of these investments. Variable life is a riskier option, but it also offers the potential for higher returns.
Determining Your Life Insurance Needs A Comprehensive Assessment
Figuring out how much life insurance you need can be daunting. There's no one-size-fits-all answer, as the ideal amount depends on your individual circumstances. A good starting point is to consider the following factors:
- Income Replacement: How much income would your family need to replace if you were no longer around? A common rule of thumb is to multiply your annual income by 7-10 years.
- Outstanding Debts: Do you have a mortgage, student loans, or other debts? Life insurance can help your family pay off these debts, preventing them from becoming a burden.
- Future Expenses: What future expenses do you want to cover, such as college tuition or retirement savings?
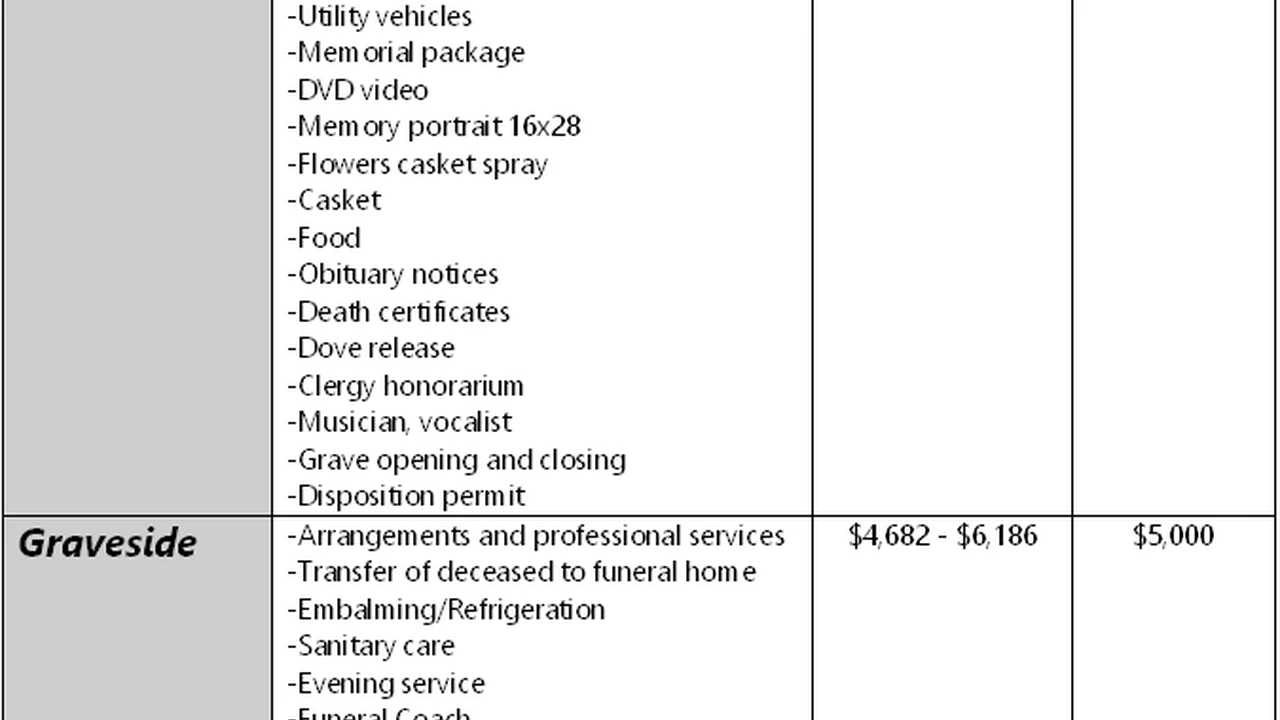
- Funeral Costs: Funeral expenses can be surprisingly high. Life insurance can help cover these costs, relieving your family of a financial burden during a difficult time.
- Existing Assets: Do you have any savings, investments, or other assets that could help support your family?
Once you've considered these factors, you can use online calculators or consult with a financial advisor to determine the appropriate amount of life insurance for your needs.
Understanding Life Insurance Premiums Factors Affecting the Cost
The cost of life insurance premiums depends on a variety of factors, including:
- Age: Younger individuals typically pay lower premiums than older individuals.
- Health: Individuals in good health typically pay lower premiums than individuals with health problems.
- Lifestyle: Smokers and individuals with risky lifestyles typically pay higher premiums.
- Type of Policy: Term life insurance is generally less expensive than permanent life insurance.
- Coverage Amount: The higher the coverage amount, the higher the premiums.
- Policy Length (for term life): Longer term lengths typically result in higher premiums.
It's important to shop around and compare quotes from different insurance companies to find the best rates. Don't just focus on the lowest price; also consider the insurer's financial stability and reputation.
Life Insurance Riders Enhancing Your Policy with Additional Benefits
Life insurance riders are optional add-ons that can enhance your policy with additional benefits. Some common riders include:
- Accelerated Death Benefit Rider: This rider allows you to access a portion of the death benefit if you are diagnosed with a terminal illness.
- Accidental Death and Dismemberment (AD&D) Rider: This rider provides an additional death benefit if you die as a result of an accident. It also pays out if you lose a limb or sight due to an accident.
- Waiver of Premium Rider: This rider waives your premium payments if you become disabled and unable to work.
- Child Rider: This rider provides coverage for your children.
- Long-Term Care Rider: This rider allows you to use a portion of the death benefit to pay for long-term care expenses.
Consider whether any of these riders would be beneficial for your specific needs and circumstances.
Choosing the Right Life Insurance Company Reputation and Financial Strength
Selecting the right life insurance company is just as important as choosing the right policy. You want to ensure that the insurer is financially stable and has a good reputation for paying claims. Here are some factors to consider:
- Financial Ratings: Look for companies with high financial strength ratings from independent rating agencies such as A.M. Best, Standard & Poor's, and Moody's.
- Customer Reviews: Read online reviews to get a sense of other customers' experiences with the company.
- Complaint Ratios: Check the company's complaint ratio with your state's insurance department. A lower complaint ratio indicates better customer service.
- Years in Business: Companies with a long track record are generally more reliable.
Don't be afraid to ask questions and do your research before making a decision.
Life Insurance for Different Life Stages Tailoring Coverage to Your Needs
Your life insurance needs will change as you go through different life stages. Here's a look at how life insurance can be beneficial at different points in your life:
Young Adults Starting Out
Even if you're young and single, life insurance can be beneficial. It can help cover funeral expenses and pay off any debts you may have. It's also a good time to lock in lower premiums while you're young and healthy.
Families with Young Children
This is a critical time to have life insurance. You need to ensure that your family is financially protected if something happens to you. Consider a term life policy to cover your mortgage, childcare costs, and future education expenses.
Empty Nesters
As your children become independent and your mortgage is paid off, your life insurance needs may decrease. However, you may still want to maintain some coverage to cover funeral expenses or leave a legacy for your loved ones.
Retirees
In retirement, your life insurance needs may be minimal. However, you may still want to consider a permanent life policy to cover estate taxes or provide for your spouse.
Specific Life Insurance Product Recommendations and Use Cases
While I cannot provide specific financial advice, I can offer general recommendations based on common scenarios. Remember to consult with a qualified financial advisor for personalized guidance.
For Young Families with Mortgages and Young Children:
Recommendation: A 20 or 30-year term life insurance policy.
Use Case: Cover the mortgage, provide for childcare expenses, and fund college education for the children if a parent passes away. The term length should align with the expected mortgage payoff date or when the children are financially independent. Consider a policy with a face value of 7-10 times the annual income of the primary earner, plus the outstanding mortgage balance. Look for policies with convertibility options, allowing conversion to a permanent policy later without a medical exam.
For Individuals with Significant Debt (Student Loans, Credit Card Debt):
Recommendation: A term life insurance policy with a coverage amount sufficient to cover the outstanding debt.
Use Case: Protect co-signers or family members from inheriting the debt. The term length should be at least as long as the expected debt repayment period. This is particularly important for student loans, as many private student loans do not have automatic discharge upon death.
For High-Net-Worth Individuals Seeking Estate Planning Solutions:
Recommendation: A permanent life insurance policy, such as whole life or universal life.
Use Case: Provide liquidity to pay estate taxes, avoid forced sales of assets, and create a legacy for future generations. These policies can also be used for wealth transfer strategies, such as irrevocable life insurance trusts (ILITs). The cash value component can also be a source of tax-deferred growth.
For Small Business Owners:
Recommendation: A combination of term and permanent life insurance, depending on the specific needs.
Use Case: Key person insurance to protect the business from the loss of a key employee, buy-sell agreements funded with life insurance to ensure a smooth transition of ownership upon death or disability of a partner, and personal life insurance to protect the owner's family. The amount of key person insurance should be based on the key employee's contribution to the company's revenue and profitability. Buy-sell agreements should be carefully structured with legal and tax advisors.
Life Insurance Product Comparisons Detailed Analysis
To illustrate the differences between policy types, consider these hypothetical scenarios and comparisons:
Scenario: A 35-Year-Old Male, Non-Smoker, in Good Health
We'll compare the estimated premiums for a $500,000 death benefit across different policy types. These are illustrative examples and actual premiums will vary based on the insurer and individual underwriting.
- 20-Year Term Life: Estimated annual premium: $300 - $400
- Whole Life: Estimated annual premium: $4,000 - $5,000
- Universal Life: Estimated annual premium: $2,500 - $3,500 (with flexible premium options)
Analysis: Term life is the most affordable option for pure death benefit protection. Whole life provides lifelong coverage and cash value growth, but at a significantly higher cost. Universal life offers a balance between cost and flexibility.
Comparison of Term vs. Whole Life:
| Feature | Term Life | Whole Life |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Period | Specific Term (e.g., 10, 20, 30 years) | Lifetime |
| Premium Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Cash Value | None | Accumulates over time |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible (policy loans, withdrawals) |
| Best For | Temporary needs, budget-conscious individuals | Long-term needs, estate planning, wealth accumulation |
Comparison of Universal vs. Variable Life:
| Feature | Universal Life | Variable Life |
|---|---|---|
| Cash Value Growth | Based on current interest rates | Based on investment performance (stocks, bonds, etc.) |
| Risk Level | Lower | Higher |
| Premium Flexibility | More flexible (adjustable premiums) | Less flexible |
| Investment Control | Limited | More control (policyholder chooses investment options) |
| Best For | Those seeking moderate growth and premium flexibility | Those seeking higher growth potential and willing to accept more risk |
Detailed Information Including Pricing and Availability
Pricing: As mentioned previously, life insurance premiums are highly individualized. To obtain accurate pricing, you'll need to provide detailed information about your age, health, lifestyle, and coverage needs to an insurance agent or broker. Online quote tools can provide estimates, but these are not binding offers.
Availability: Life insurance is widely available through various channels:
- Independent Insurance Agents: Represent multiple insurance companies and can provide unbiased advice.
- Captive Insurance Agents: Represent a single insurance company.
- Online Insurance Brokers: Offer quotes from multiple insurers online.
- Directly from Insurance Companies: Some companies sell policies directly to consumers.
Factors Affecting Pricing Beyond the Basics:
- Build (Height and Weight): Insurance companies use height and weight charts to assess risk. Being significantly overweight or underweight can impact premiums.
- Family Medical History: A family history of certain diseases (e.g., heart disease, cancer) can increase premiums.
- Driving Record: A history of traffic violations or accidents can affect premiums.
- Hobbies and Occupations: Engaging in risky hobbies (e.g., skydiving, scuba diving) or having a dangerous occupation can increase premiums.
Guaranteed Insurability Rider (GIR): This rider allows you to purchase additional life insurance coverage at specified intervals without providing further proof of insurability. It's a valuable option for young adults who anticipate needing more coverage in the future.
Return of Premium (ROP) Term Life Insurance: This type of term life insurance returns all of your premiums if you outlive the term. While it sounds appealing, ROP policies typically have significantly higher premiums than traditional term life policies.
Navigating the Application Process A Step-by-Step Guide
Applying for life insurance typically involves the following steps:
- Get a Quote: Obtain quotes from multiple insurers to compare rates.
- Complete the Application: Provide detailed information about your health, lifestyle, and financial situation.
- Medical Exam: Many insurers require a medical exam to assess your health. This may include blood and urine tests, as well as a physical examination.
- Underwriting: The insurer will review your application and medical exam results to determine your risk level and set your premiums.
- Policy Delivery: If your application is approved, you'll receive your policy documents. Review them carefully to ensure that they accurately reflect your coverage and benefits.
- Payment of Premium: Pay your initial premium to activate your coverage.
Common Reasons for Application Denial:
- Pre-existing Medical Conditions: Serious health issues can lead to denial or higher premiums.
- Inaccurate or Incomplete Information: Providing false or misleading information on your application can result in denial.
- High-Risk Lifestyle: Engaging in dangerous activities can increase your risk profile.
Life Insurance Tax Implications Understanding the Rules
Life insurance benefits are generally tax-free to beneficiaries. However, there are some tax implications to be aware of:
- Estate Taxes: Life insurance proceeds may be subject to estate taxes if your estate is large enough.
- Cash Value Growth: The cash value growth in permanent life insurance policies is tax-deferred.
- Policy Loans: Policy loans are generally tax-free, but interest may be charged.
Consult with a tax advisor to understand the specific tax implications of life insurance in your situation.
Common Life Insurance Myths Debunked
There are many misconceptions about life insurance. Let's debunk some common myths:
- Myth: Life insurance is only for older people. Reality: Life insurance is beneficial at any age, especially if you have dependents or debts.
- Myth: Life insurance is too expensive. Reality: Term life insurance is generally affordable, especially for young and healthy individuals.
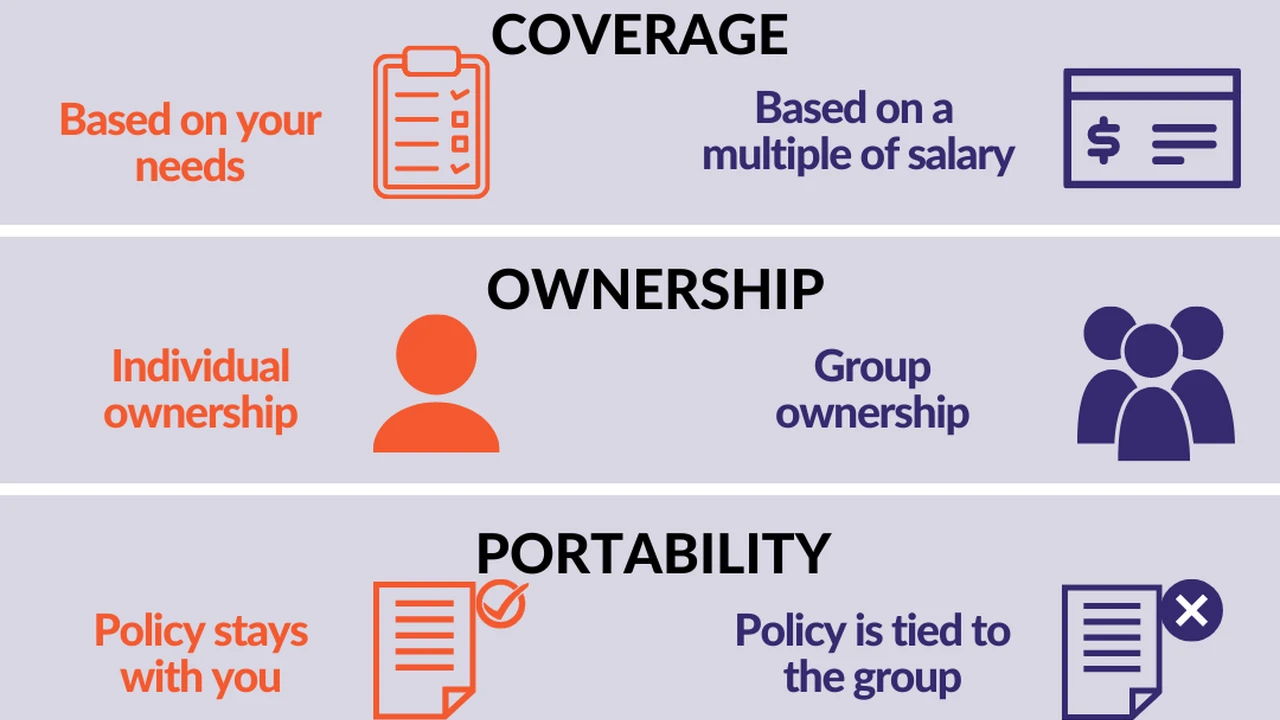
- Myth: I don't need life insurance because I have life insurance through my employer. Reality: Employer-sponsored life insurance may not be sufficient to meet your needs, and it may not be portable if you leave your job.
- Myth: I don't need life insurance because I'm single. Reality: Life insurance can help cover funeral expenses and pay off any debts you may have, even if you don't have dependents.
Making Informed Decisions About Life Insurance Securing Your Family's Future
Life insurance is a crucial component of financial planning, providing a safety net for your loved ones in the event of your death. By understanding the different types of policies, assessing your needs, and shopping around for the best rates, you can make informed decisions that secure your family's future. Remember to consult with a qualified financial advisor to receive personalized guidance tailored to your specific circumstances.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/277019-baked-pork-chops-with-cream-of-mushroom-soup-DDMFS-beauty-4x3-BG-7505-5762b731cf30447d9cbbbbbf387beafa.jpg)